Syndromes
with Ocular Manifestations
Syndrome List (A-Z) (common/important
in bold)
A | B | C | D | E | F
| G | H | I-J-K | L | M | N | O
| P | R | S |T
| U-V | W | X-Y-Z
Index
of Ocular Findings
A
B
- Baller-Gerold
-
Bannayan-Riley-Smith (Ruvalcaba-Myhre,
Riley-Smith)
- Barber-Say
- Bardet-Biedl
- Bassen-Kornzweig
disease
-
Beals
- Beckwith-Wiedemann
- Berardinelli-Lipodystrophy
- Berman (Sialolipidosis, Mucolipidosis type IV)
- Bernheimer-Seiteberger disease (Gangliosidosis
GM2 Type III)
- Beta-Glucuronidase deficiency (Sly,
Mucolipidosis type VII)
- Bird-Headed Dwarfism (Seckel)
- Blepharophimosis
- Borjeson-Forssman-Lehmann
- Brachmann-de Lange (Cornelia de Lange)
- Branchio-Oculo-Facial
C
- Caffey Pseudo-Hurler (Gangliosidosis GM1
Type I)
-
Campomelic Dysplasia
- Camurati-Englemann
- Cardiac-Limb (Holt-Oram)
- Cardio-Facio-Cutaneous
- Carpenter
- Cat-Eye (Schmid-Fraccaro)
- Cerebral Giantism (Sotos)
- Cerebro-Oculo-Facio-Skeletal (Pena-Shokeir, Type
II)
- Cerebro-Hepato-Renal (Zellweger)
- Cervico-Oculo-Acoustic (Widervanck)
- CHARGE Association
- Cheney
(Hajdu-Cheney, Acro-Osteolysis)
- Chondrodysplasia Punctata, AR/X-linked
- Cleft lip Sequence
- Cleidocranial Dystosis
- Clouston
- Cockayne, Type I
- Coffin-Lowry
- Coffin-Siris
- Cohen
- Chrondodystophica myotonia (Schwart-Jampel type
1)
- Cornelia de Lange (Brachmann-de Lange)
- Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia- Lenz Majewski type
(Lenz-Majewski Hyperostotic Dwarfism)
- Craniofrontonasal Dysplasia
- Craniometaphyseal Dysplasia
-
Craniosynostosis
- Cri-du-Chat (Deletion 5p)
- Crouzon
- Cryptophthalmos (Frasier)
D
- De Grouchy
- Deletion 2q
- Deletion 3p
- Deletion 4p (Wolf-Hirschhorn)
- Deletion 4q
- Deletion 5p (Cri-du-Chat)
- Deletion 9p
- Deletion 11p (WAGR
syndrome)
- Deletion 11q (Jacobsen)
- Deletion 13q
- Deletion 15q
maternal (Angelman)
- Deletion 15q paternal (Prader-Wili)
- Deletion 18p
- Deletion 18q (De Grouchy)
- De Morsier (Septo-Optic Dysplasia)
- Derry (Gangliosidosis GM1
Type II)
- Desbuquois (Larsen)
- Digeorge Sequence
- Distal Arthrogryposis Type II
- Distichiasis-Lymphedema
- Donohue (Leprechaunism)
- Down (Trisomy 21)
- Duane/Radial dysplasia
- Dubowitz
- Duplication 3q
- Duplication 4p
- Duplication 9p
- Duplication 10q
- Duplication 15q
- Dyskeratosis Congenita (Zinsser-Cole Engman)
E
- Ectopia Lentis et Pupillae
- Ectodermal dysplasia 1 (Hypohidrotic Ectodermal
Dysplasia)
- Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting I
- Edwards (Trisomy 18)
- Ehlers-Danlos
- Elejalde (Acrocephalopolydactylous
Dysplasia)
- Encephalofacial Angiomatosis (Sturge-Weber)
- Escobar
F
- Facio-Digito-Genital
Dysplasia
- Facio-oculo-auriculo-vertebral dysplasia
(Goldenhar)
- Fanconi Pancytopenia
- Femoral Hypoplasia-Unusual Facies
- Fetal Akinesia sequence (Pena-Shokeir type I)
- Fetal Face (Robinow)
- FG (Opitz-Kaveggia)
- Focal dermal hypoplasia (Goltz)
- Fragile X (Martin-Bell)
- François Dyscephalic (Hallerman-Streiff,
Oculomandibulodyscephaly)
- Fraser (Cryptophthalmos)
- Freeman-Sheldon (Whistling Face)
- Frontometaphyseal
G
- Gaucher
- Goldenhar
- Gangliosidoses
- Geleophysic Dysplasia (Acrofacial dysplasia)
- Genee-Widemann (Miller, Postaxial Acrofacial
Dystosis)
- Gillespie
(Aniridia-Cerebellar ataxia-Mental deficiency)
- Goldenhar (Facio-oculo-auriculo-vertebral
dysplasia)
- Goltz (Focal dermal hypoplasia)
- Goodman
(Acrocephalopolysyndactyly Type 4)
- Gorlin (Nevoid basal cell carcinoma)
- Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly
H
- Hajdu-Cheney
(Cheney, Acro-Osteolysis)
- Hallermann-Streiff (François Dyscephalic,
Oculomandibulodyscephaly)
- Hay-Wells Syndrome of
Ectodermal Dysplasia (Ankyloblepharon-Ecterdermal Dysplasia-Clefting)
- Hepatolenticular
degeneration (Wilson Disease)
- Holt-Oram (Cardiac-limb)
- Homocystinuria
- Hunter (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II)
- Hurler (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I H)
- Hurler-Scheie (Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I
H/S)
- Hutchinson-Gilford (Progeria)
- Hypochondroplasia
- Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia (Ectodermal
Dysplasia 1)
- Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, autosomal
dominant type (Rapp-Hodgkin Ectodermal Dysplasia)
- Hypomelanosis of Ito (Incontiential Pigmentosa
Achromians)
- Hypophosphatasia
I-J-K
- Incontientia Pigmenti (Bloch-Sulzberger)
- Incontiential Pigmentosa Achromians
(Hypomelanosis of Ito)
- Jackson-Weiss (Craniosynostosis-Foot Defects)
- Jacobsen (Deletion 11q)
- Jarcho-Levin (Spondylothroacic Dysplasia)
- June Thoracic Dystrophy
- Johanson-Blizzard
- Joubert
- Kabuki (Niikawa-Kuroki)
-
Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness (Kid)
- Kid (Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness)
- Killian-Teschler-Nicola (Pallister-Killian)
- Kivlin-Krause (Peters Anomaly with Short-limb
dwarfism)
- Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber
(Angio-Osterohypertrophy)
- Kniest dysplasia (Metatrophic Dwarfism II)
L
- Lacrimo-Auriculo-Dento-Digital; LADD
(Levy-Hollister)
- Langer-Giedion (Tricho-Rhino-Phalangeal)
- Larsen (Desbuquois)
- Leber's Congential Amaurosis
- Lenz-Majewski Hyperostotic Dwarfism
(Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia- Lenz Majewski type)
- Leopard (Multiple Lentigines)
- Leprechaunism (Donohue)
- Leroy I-Cell (Mucolipidosis type II)
- Levy-Hollister (Lacrimo-Auriculo-Dento-Digital; LADD)
- Linear Nevus Sebaceous of Jadassohn
- Lipodystrophy, partial, with Reiger Anomaly,
short stature and Insulinopenic Diabetes Mellitus
- Louis
Bar (Ataxia Telangectasia)
- Lowe (Oculocerebrorenal)
M
- Marden-Walker
- Marfan
- Marfanoid Craniosynostosis (Shprintzen-Goldberg
Craniosynostosis)
- Maroteaux-Lamy (Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI)
- Martin-Bell (Fragile X)
- Marshall
- Marshall-Smith
- Melnick-Needles Osteodysplasty
- Metatrophic Dwarfism II (Kniest Dysplasia)
- Midas (Microphthalmia with Linear Skin Defects)
- Miller (Genee-Widemann, Postaxial Acrofacial
Dystosis)
- Miller-Dieker Lissencephaly
- Möbius
- Mohr (OFD Syndrome type II)
- Morquio (Mucopolysaccharidosis type IV)
- Mucolipidoses
- Sialidosis, Spranger (Mucolipidosis type I,
suptypes I,II)
- Leroy I-Cell (Mucolipidosis type II)
- Pseudo-Hurler Polydystrophy (Mucolipidosis type
III)
- Sialolipidosis (Berman, Mucolipidosis type IV)
- Sly (Beta-Glucuronidase deficency, Mucolipidosis
type VII)
- Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS)
- Hurler (MPS I H)
- Hurler-Scheie (MPS I H/S)
- Scheie (MPS I S)
- Hunter (MPS II)
- Sanfilippo (MPS III)
- Morquio Syndrome (MPS IV)
- Maroteaux-Lamy (MPS VI)
- Mulibrey Nanism (Perheentupa)
- Multiple Lentigines (Leopard)
- Multiple Synostisis (Symphalangism)
N
O
- Oculocerebrorenal (Lowe)
- Oculodentodigital (Oculodentoosseous dysplasia)
- Oculomandibulodyscephaly (Hallerman-Streiff,
François Dyscephalic)
- OFD syndrome Type II (Mohr)
- Opitz type I,II (Opitz-Frias)
- Opitz-Kaveggia (FG)
- Oral-Facial-Digital 1 (OFD)
- Oromandibular-Limb hypogenesis
spectrum (Aglossia-Adactyly)
- Osteogeneis Imperfecta type I
- Oto-Palato-Digital type I (Taybi)
P
- Pachyonychia Congenita type I
- Pallister-Hall
- Pallister-Killian (Killian-Teschler-Nicola)
- Patau (Trisomy 13)
- Pena-Shokeir type I (Fetal Akinesia sequence)
- Perheentupa (Mulibrey Nanism)
- Peters Anomaly-isolated
- Peters Anomaly with other ocular defects
-
Peters Anomaly with Short-limb dwarfism
(Kivlin-Krause)
- Peters-Plus
- Pfeiffer Type I,II, III (Acrocephaloysyndactyly
type 5)
- Poikilodermal Congenitale (Rothmund-Thompson)
- Postaxial Acrofacial Dystosis (Genee-Widemann,
Miller)
- Prader-Wili (Deletion 15q)
- Progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford)
- Proteus
- Pseudo-Hurler Polydystrophy (Mucolipidosis type
III)
R
- Radial Aplasia-Thrombocytopenia syndrome (TAR)
- Rapp-Hodgkin Ectodermal Dysplasia (Hypohidrotic
ectodermal dysplasia, autosomal dominant type)
- Retinoblastoma
- Reiger Type I,II
- Robinow (Fetal Face)
- Rosenthal-Kloepfer Syndrome
(Acromegaloid Phenotype-Cutis Verticis Gyrata-Corneal Leukoma)
- Rothmund-Thompson (Poikilodermal Congenitale)
- Rubinstein-Taybi
S
- Saethre-Chotzen (Acrocephaloysyndactyly type 3)
- Sandoff disease (Gangliosidosis GM2
Type II)
- Sanfilippo (Mucopolysaccharidosis III)
- Scheie (Mucopolysaccharidosis IS)
- Schinzel-Giedion Midface Retraction
- Schwart-Jampel type 1 (Chrondodystophica myotonia)
- Sclerosteosis
- Seckel (Bird-Headed Dwarfism)
- Septo-Optic Dysplasia (De Morsier)
- SHORT
- Shprintzen (Velo-Cardio-Facial)Shprintzen-Goldberg Craniosynostosis (Marfanoid
Craniosynostosis)
-
Sialidosis (Spranger, Mucolipidosis type I)
- Sialolipidosis (Berman, Mucolipidosis type IV)
- Simple Ectopia Lentis
- Simpson-Golabi-Behmel
- Sly (Beta-Glucuronidase deficency, Mucolipidosis
type VII)
- Smith-Lemli-Opitz type I
- Smith-Magenis
- Sotos (Cerebral Giantism)
- Spondylocarpotarsal Synostosis
- Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Congenita
- Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Tarda
- Spondylothroacic Dysplasia (Jarcho-Levin)
- Spranger (Sialidosis Mucolipidosis type I)
- Stickler
- Sturge-Weber (Encephalofacial Angiomatosis)
- Symphalangism (Multiple Synostisis)
T
- TAR (Radial Aplasia-Thrombocytopenia syndrome)
- Tay-Sachs disease (Gangliosidosis GM2
Type I)
- Taybi (Oto-Palato-Digital type I)
- Thalassemia
- Treacher-Collins
- Tricho-Rhino-Phalangeal (Langer-Giedion)
- Triploidy Type II
- Trisomy 8 (Warkany)
- Trisomy 9
- Trisomy 13 (Patau)
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards)
- Trisomy 21 (Down)
- Turner (XO)
U-V
W
- Waardenburg Anophthalmia
- Waardenburg
- WAGR (Deletion
11p)
- Walker-Warburg
- Warkany (Trisomy 8)
- Weaver
- Weill-Marchesani
- Werner
- Whistling Face (Freeman-Sheldon)
- Williams (Williams-Beuren)
- Wilson Disease
- Wolf-Hirschhorn (Deletion 4p)
X-Y-Z
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum
- X-linked Alpha Thalassemia/Mental retardation
- XO (Turner)
-
XXX, XXXX, XXXXX
- XXXY, XXXXY
- Yunis-Varon
- Zellweger (Cerebro-Hepato-Renal)
- Zinsser-Cole Engman (Dyskeratosis congenita)
Aase-Smith Syndrome
Main Features
- Triphalangeal thumbs
(finger-like)
- Congenital hypoplastic
anemia
Eye Findings
- Downslanting palpebral
fissures: euryblepharon, occasionally
- Retinopathy occasionally
Other Findings
- Ventricular septal defect
Etiology
- Most likely autosomal
recessive
- 10 cases reported
- Might be the same as
Diamond-Blackfan Syndrome
Reference: OMIM 205600
Abetaliproproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig disease)
Main Features
- Intestinal fat
malabsorption, onset of symptoms 5-15 years of age
- Ataxia, psychomotor
retardation, steatorrhea, blurred vision or nyctalopia
Eye Findings
- Nyctalopia and decreased
vision
- ERG findings are
apparent before retinal changes visible, decreased maximal combined
response
- Pigmentary
retinal degeneration in 50%, usually develops in early teens
- Retinitis
Pigmentosa-like changes in some
- Others have
retinitis punctata albescens-like picture
- Macula may be
spared
- Vitamin A and E
supplementation can improve retinal functioning
- Strabismus
- Nystagmus
- Angioid streaks
- Subretinal
neovascularization
- Cataract
- Ptosis
Etiology
- Autosomal Recessive
- Absence of apolipoprotein B
synthesis
- Defect of microsomal
triglyceride transfer protein of hepatocytes and enterocytes
- Gene locus 4q22-q24
Other Findings
- Fat malabsorbtion with fat
vitamin deficencies
- Spinocerebellar
degeneration, peripheral neuropathy
- Acanthotic red blood cells,
anemia
- Cardiac dysarrhythmias
- Plasma lipids levels are
abnormal: low serum cholesterol and no serum beta lipoprotein
Reference
- OMIM 200100
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and
Strabismus eds. Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. pp. 101, 1029
Ablepharon-Macrostomia Syndrome
Main Features
- Macrostomia, absent
zygomatic arch, absent eyebrows and eyelids
Eye Findings
- Absent eyebrows and upper
and lower eyelids and lashes- (ablepharon or severe microblepharon)
- Corneal exposure with
erosions/abrasions necessitating eyelid reconstruction
Etiology
- Autosomal or x-linked
recessive
- Few cases
- Failure of lip fusion gives
large mouth
Other Findings
- Sparce hair
- Thickened skin
- small ears
- small anteverted nostrils
- finger contractures
- hearing loss
- absent or small nipples
- genital anomalies-
ambiguous genetalia
- delayed language
development
- over lap with Barber-Say
Syndrome
References
- OMIM 200110
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and
Strabismus eds. Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. pp. 101, 1029
Abruzzo-Erickson Syndrome
Acrocallosal Syndrome
Acrocephalopolysyndactyly Type 4 (Goodman) Syndrome
Acrodephalopolydactylous
Dysplasia
Acrodysostosis
Acro-Fronto-Facio-Nasal
Dystosis
Acromegaloid
Facial Appearance
Acromegaloid Phenotype-Cutis Verticis Gyrata-Corneal
Leukoma (Rosenthal-Kloepfer) Syndrome
Acromesomelic
Dwarfism
Acromicric
Dysplasia
Acro-Osteolysis (Hajdu-Cheney, Cheney) Syndrome
Acro-Reno-Ocular Syndrome
Adams-Oliver Syndrome
Aicardi
Syndrome
Main Features
Eye Findings
- Anterior Segment:
Microcornea with or without coloboma
- Posterior Segment:
Chorioretinal Lacunae radiating from optic disc most often
- absence of
neurosensory retina, attenuated choroid, RPE hyperplasia
- Photoreceptor
rosettes and photoreceptor inversions
- Visual prognosis
better without lacunae
- Gross motor and
language worse if many large lacunae
Etiology
- Xp22 mutation
- X-Linked Dominant
- Lethal in Males
Other Findings
- Neuro: Mental retardation,
Characteristic EEG
- ENT: Cleft Lip and Palate
- Skin: Scalp lipomas,
cavernous hemangiomas
- Bone: Vertebral and rib
abnormalities
Reference
- OMIM 304050
- McMahon RG, Bell
RA, Moore GRW, Ludwin SK. Aicardi's Syndrome, A Clinicopathologic Study.
Arch Ophthalmol 102; 250-53,1984
Alagille (Arteriohepatic Dysplasia) Syndrome
OMIM #118450
From a study of 22 children with Alagille syndrome and 23 of their parents, Hingorani et al.
(1999) concluded that Alagille syndrome is associated with a characteristic
group of ocular findings without apparent serious functional significance and
probably unrelated to fat-soluble vitamin deficiency. Simple ophthalmic
examination of children with neonatal cholestatic jaundice and their parents
should allow early diagnosis of Alagille syndrome, eliminating the need for
extensive and invasive investigations. The most common ocular abnormalities in
patients were posterior embryotoxon (95%), iris abnormalities (45%), diffuse
fundus hypopigmentation (57%, a previously unreported finding), speckling of
the retinal pigment epithelium (33%), and optic disc anomalies (76%).
Microcornea was not associated with large refractive errors, and visual acuity
was not significantly affected by these ocular changes. Ocular abnormalities,
including posterior embryotoxon, iris abnormalities, and optic disc or fundus
pigmentary changes, were detected in 1 parent in 36% of cases. 
Albinism
Main Features
- Oculocutaneous
Albinism (OCA): Hypopigmentation of skin and hair with
characteristic eye findings
- Ocular Albinism
(OA): Normal skin and hair pigmentation
with characteristic eye findings
- See Albinism in Retina notes
for more information
Eye Findings
- Refractive error: significant
myopia, hyperopia and/or astigmatism
- Motility: Nystagmus,
esotropia
- Vision: Variable
20/40-20/200
- Iris: Transillumination
defects (from complete lack of pigmentation in OCA1 to variable small
defects in OA)
- Fundus: Hypopigmentation,
foveal hypoplasia
- Optic nerve function:
Abnormal visual evoked potentials (representing abnormally high amount of
decussation of ganglion cell fibers)
Etiology : OCA1A (commonly recognized type) occurs in
1/40,000 with 1/100 are carriers, OCA: autosomal recessive, OA: X-linked
- OCA1A: Two
TYR gene mutations (11q14-q21)
causing no tyrosinase to be produced; no melanin
- OCA1B: Two
TYR gene mutations causing at least one copy of a partially active
tyrosinase enzyme: less melanin
- OCA2: P
gene mutation (15q11.2-q12)
hair pigmented but not skin, some iris pigment
- OCA3:
TYRP1 gene mutation (9p23)
described in those of african descent
- OCA4: MAPT
gene mutation (5p)
one human case
- Hermansky-Pudlak
syndrome: mutation in any of HPS1 (10q23.1),
HPS2 (5q13)
, HPS3 (3q24),
HPS4 (22q11.2-q12.2)
- Chediak-Higashi
syndrome: chromosome 1
- OA1: OA1
gene mutations (Xp22): males with normal hair and skin pigment, abnormal
melanosome production
Other Findings
- OCA1A: No
pigment of hair or skin, coarse rough skin, unpigmented nevi, solar
keratoses (premalignant) basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas (actually
quite rare due to good prevention), skin melanocytes are present but
melanoma rare
- OCA1B: white to very light
hair and skin at birth with variable amounts of darkening, pigmented nevi
and freckles can develop
- OCA2: Pigmented hair at
birth, no generalized skin pigmentation but pigmented nevi and freckles
can develop
- Hermansky-Pudlak
syndrome: lethal subtype
- Chediak-Higashi
syndrome: lethal subtype
- OA1: giant melanosomes on
skin biopsy if preformed, defect is in melanosome production, can have
late onset sensorineural deafness, female carriers have mosaic
pigmentation of peripheral fundus
- OA2: Families from Aland
Islands in the Sea
of Bothnia, female carriers do
not have a mosaic pattern, possibly a type of CSNB (310500),
(Xp11.4-p11.23)
OMIM: 300600,
- OA3: ocular albinism that
is autosomal recessive: OMIM: 203310
(6q13-q15)
or (15q11.2-q12)
- OA with sensorineural
deafness: OMIM: 103470
(11q14-q21,
3p14.1-p12.3) Waardenberg Syndrome type II with ocular albinism,
mutation in the transcription factor MITF which regulates the TYR gene
References
- Duane's Ophthalmology:
Traboulsi EI, Green WR, O'Donnell Jr FE,.The eye in Albinism. 1998 CD ROM
edition.
- Creel DJ, Summers CG, King
RA. Visual anomalies associated with albinism. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet
11:193-200,1990
- OMIM: OCA1:203100,
OCA2: 203200,
OCA3: 203290,
OCA4: 606574,
Hermansky-Pudlak: 203300,
OA1: 300500
Albright
Hereditary Osteodystrophy
Alport Syndrome
Main Features
- Nephritis, anterior
lenticonus and deafness
Eye Findings
- Posterior polymorphous
corneal dystrophy
- Anterior Lenticonus
- Cataracts
- Macular Pigment
epitheliopathy- white or yellow flecks in the macula
Etiology
- Mutation in on of type IV
collagen genes, Chromosome 2 and X
- X-linked (80%)- COL4A5: OMIM
link
- Autosomal Recessive (15%)-
COL4A3: OMIM
link
- Autosomal Dominant (5%)-
COL4A4: OMIM
link
Other Findings
- Hearing loss- not
congenital, detectable in late childhood, progressive and 80-90% nerve
deafness by age 40 in X linked disease
- Hemorrhagic nephritis-
microscopic hematuria, 50% get end stage renal disease by age 30 and 90%
by age 40
References
Aniridia-Cerebellar ataxia-Mental deficiency (Gillespie) Syndrome
Ankyloblepharon-Ecterdermal Dysplasia-Clefting (Hay-Wells) Syndrome
Angelman
(Deletion 15q) Syndrome
Angio-Osterohypertrophy (Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber) Syndrome
Anophthalmia with Limb Anomalities (Waardenburg Anophthalmia)
Antley-Bixler Syndrome
Apert Syndrome
Ataxia-Telangiectasia
Syndrome (Louis-Bar
Syndrome)
Barber-Say Syndrome
Reference
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
(Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Syndrome)
Main Features
Deletion 11p (WAGR
Syndrome)
Facio-Digito-Genital
Dysplasia Syndrome (Aarskog Syndrome)
Main Features
- Short stature,
brachydactyly, shawl scrotum
Eye Findings
- Hypertelorism (90%)
- Ptosis (50%)
- Downslanting palpebral
fissures
- Strabismus
- Hyperoptic astigmatism
- latent nystagmus
- blue sclera
- posterior embryotoxin
- corneal enlargement
Etiology
- X-linked recessive, linked
to Xp11.21
- Female carriers have minor
manifestations
- 100 cases reported
Other Findings
- Broad upper lip, anteverted
nostrils
- Osteoconditis dessicans
- Stretchable skin
References
- OMIM 100050,
*305400
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and
Strabismus eds. Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p.1029
FG Syndrome (Opitz-Kaveggia)
Main Features
- Mental deficiency, delayed
motor development, short stature, macrocelpahy, prominent forhead, small
ears, facial skin wrinkling, sparce hair
- Imperforate anus, broad
thumbs and great toes
Eye Findings
- Strabismsus, Hypertelorism,
Epicanthus, Downward slanting palpebral fissures, Medial eyebrow flare
Etiology
Other Findings
- Occasionally
craniosynostosis
References
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus eds.
Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p.1038
- OMIM: %305450
Gaucher
Syndrome
Main Features
- Hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, brusing and bone
pain
Eye Findings
- Strabismus
- Oculomotor Apraxia
GM1
Gangliosidosis Type I (Severe Infantile Type) (Caffey
Pseudo-Hurler Syndrome, Familial Neuorvisceral Lipidosis)
Main Features
-
Infancy onset Lisosome sphingolidosis
-
Hypotonia, seizures,
dysmophism, organomegaly
Eye Findings
- Cherry-red spot (50%)
- Nystagmus
- tortuous conjunctival vessels with saccular aneurisms
- papilledema
- optic atrophy
- corneal clouding rare
- high myopia
Etiology
- Defect in GM1 ß-galactosidase-1- all
three isoenzymes are missing (A,B, and C)
- Diagosis confirmed by assay of ß-galactosidase
in peripheral leukocytes
- Prenatal diagnosis on cultured amniotic fluid cells
- Gene map locus: 3p21.33
- Autosomal recessive
Other findings
- Facial and peripherial edema
- Kyposis, joint limitation, thick wrists, contractures of elbows and
knees, claw hand
- Congestive heart failure, hepatosplenomegaly
- Death usually in early infancy (by age 2)
References
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus eds.
Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p. 971, 1039
- OMIM:
+23050
GM1
Gangliosidosis Type II (Juvenile Type)
(Derry Disease)
Main Features
-
Locomotor ataxia usually first sign, followed by progressive psychomotor
deterioration and seizures
- Decerebrate and rigid by end
of second year of life
- Death by age 3-10 years
Eye Findings
- Nystagmus
- Esotropia
- Cherry Red Spot
- Optic Atrophy
Etiology
- Defect in GM1 ß-galactosidase-1- missing
B and C isoenzymes
- Autosomal recessive
- Gene map locus: 3p21.33
References
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus eds.
Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p. 971, 1039
- OMIM
#23060
GM2 Gangliosidosis Type I (Tay-Sachs
disease)
Main Features
-
Child becomes apathetic, hypotonic and sensitive
to sound (abnormal startle reflex)
-
Progressive neurological deterioration and
seizures
-
Death usually by 24 to 30 months of age
Eye Findings
-
Cherry red spot by 6 months of age- can disappear
as ganglion cells die
-
Decreased vision by 12-18 months of age
-
Nystagmus
-
Optic atrophy
-
Narrowing of retinal vessels
Etiology
-
Hexosaminidaze A isoenzyme deficiency
-
Gene map locus: 15q23-q24
-
Autosomal recessive
-
Carrier 1:300 in non Jews and 1:30-40 in Jews of
European extraction in US and Canada
-
Incidence 1:4000 in Ashkenazi Jews
References
- Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus eds.
Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p. 971, 1039
-
OMIM:
#272800
Goldenhar
Syndrome
- solid limbal dermoids
- lid colobomas
- pre-auricular skin tags
- vertebral abnromalities
Incontinentia Pigmenti
(Bloch-Sulzbeger syndrome)
Main Features
- Involves skin, brain and eyes
- X-Linked dominant, usually lethal to males
- Skin normal at birth but erythema and bullae develop in first few days
of life usually on extremities
- Verrucous changes at two months of age then small hyperpigmented macules
on trunk appear
Eye Findings
(in 25%-33%)
- Proliferative retinal vasculopathy that resembles retinopathy of
prematurity
- At birth incomplete peripheral vascularization develops into abnormal
vascular shunts and neovascular membranes
- Retinal detachment often develops
- Retrolental membrane formation (pseudoglioma)
- Microphthalmos, cataract, glaucoma, optic atrophy, strabismus, nystagmus
- Treated like retinopathy of
prematurity
Etiology
- Caused by mutations in the NEMO gene
Xq28
Other Findings
- CNS abnormalities (33%)
- microcephaly, hydrocephalus,seizures, mental deficiency
- Dental abnormalities (66%)
- missing or malformed teeth
- Less common: scoliosis, skull deformities, cleft palate, dwarfism
References
- Catalano RA. Incontientia pigmenti.AM J Ophthalmol. 1990;110:696-700
- OMIM:
#308300
Joubert
Syndrome
Main Features
- Cerebellar vermis hypoplasia or aplasia,
episodic tachypnea ("panting like a dog") and apnea in infancy, jerky
eye movements, hypotonia, developmental delay
Eye Findings
- Ocular Motor Abnormalities
- Absent smooth pursuit
- Hypometric saccades with prolonged latency; they
change direction of fixation by turning their heads
- Nystagmus – pendular, rotary, horizontal,
see-saw, torsional
- Congenital Retinal Dystrophy (in majority of
patients; some definitely have normal appearing fundi)
- Progressive chorioretinal pigmentary changes
including reports of "mottling" in periphery
- Chorioretinal Coloboma
- Attenuation of retinal arterioles
- Nonrecordable / attenuated ERG, but Preserved
flash and pattern VEPs (Differentiates from
LCA)
- Rod photoreceptors are more severely affected
than cones
- May have good Best Corrected Visual Acuity –
reports of 20/40 (also better than LCA)
-
Those with Retinal dystrophy also have Renal
cysts and other kidney disease
- Ptosis – Bilateral or Unilateral
- Strabismus
- Supranuclear Ocular motor palsies
Etiology
-
Autosomal Recessive
-
First described in 1969, by 1991, 94 patients
reported
-
More commonly reported in cultures of
consanguinity, although distributed worldwide
Other Findings
-
Neuro: Mental retardation, ataxia
-
Respiratory: Episodic tachypnea and apnea that
improves with age
-
Renal: Renal cysts, inflammation, sclerosis, can be deadly
-
GI: protruding tongue, tongue tumors, pyloric
stenosis, duodenal atresia, hepatic inflammation
-
Bone: Polydactyly
Differentiating Joubert’s from Leber’s
Congenital Amaurosis
-
Both have nonrecordable or severely attenuated
ERG, but Joubert’s has recordable (less than normal) flash and pattern VEPs
-
Joubert’s generally has better Visual acuity
References
-
Lambert, et al. Arch Ophth 1989;107:709-713
-
Sztriha, et al. Ped Neurol 1999; 20:274-281
-
Saraiva, Am J of Med Genetics 1992; 43:726-731
-
OMIM 213300, 608091
Mucopolysaccharidosis II
(MPS II; Hunter)
Main Features
- Dystosis mulitplex, organomegaly, coarse facies, psychomotor retardation
- Pebbly skin lesions on back, upper arms, and thigh
Eye Findings
- Pigmentary Retinopathy
- Coneal clouding (rare)
- Penetrating Keratoplasty if vision warrants but recurrence in graft
possible
Etiology
- Defect in iduronate 2-sulfatase leading to build up of lysosome
mucopolysaccharides
- X-linked recessive
- 1: 100,000 live births
Other Findings
- hydrocephalus
- stiff joints with contractures
- valvular heart disease
- obstructive airway disease
- chronic diarrhea
- inguinal herneas
- hearing impairment
- wide spaced teeth
- hypertrichosis
- death may be in 2nd decade in severe type, or as late as 5th decade in
mild form
References
-
Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus eds.
Wright KW, Spiegel PH. 2nd ed. p. 404, 972, 1041
- OMIM
+309900
Nager Syndrome (Acrofacial
dystosis 1, Nager Type)
Noonan Syndrome
Lee et al. (1992) reviewed the ophthalmologic and orthoptic
findings in 58 patients with Noonan syndrome. External features were
hypertelorism (74%), downward sloping palpebral apertures (38%), epicanthal
folds (39%), and ptosis (48%). Orthoptic examination revealed strabismus in
48%, refractive errors in 61%, amblyopia in 33%, and nystagmus in 9% of cases.
Anterior segment changes, found in 63% of patients, included prominent corneal
nerves (46%), anterior stromal dystrophy (4%), cataracts (8%), and panuveitis
(2%). Fundal changes occurred in 20% of patients and included optic nerve head
drusen, optic disc hypoplasia, colobomas, and myelinated nerve fiber layer. Lee et al. (1992)
recommended early ophthalmic examination of children with Noonan syndrome.
Oromandibular-Limb hypogenesis spectrum (Aglossia-Adactyly
syndrome)
Pfeiffer Syndrome (Acrocephaloysyndactyly
type 5)
Rubinstein-Taybi
Syndrome
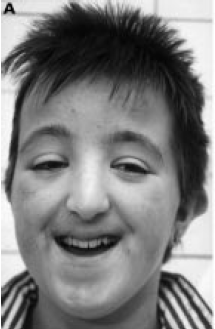
Main Features
- Mental Retardation, Speech difficulty, broad thumbs and toes, often
medially deviated
Eye Findings
- External: Down-slanting palpebral fissures (88%), Heavy eyebrows or high
arched (76%), long eyelashes (89%), epicanthal folds (55%)
- Abnormal ERG (78%)
- Decreased Cone or Cone & Rod response
- Macular abnormalities (75%)
- Hypoplasia, pigment abnormalities, increased red color, absent foveal
reflex
- Abnormal VEP (60%)
- Strabismus (70%)
- Refractive Error (50%)
- NLD obstruction (40%)
- Ptosis (36%)
- Glaucoma (30%-5%)
- Coloboma (20%-6%)
- Congenital Cataract (20-6%)
- High Myopia (10%)
- Optic atrophy/disc abnormalities (10%)
- Chorioretinal Dystrophy (5%)
- Microphthalmia (5%)
- Nystagmus (4%)
- Ectopia Lentis (<1%)
Etiology
- 1/100,000 newborns
- Autosomal Dominant
- Many from Chromosome 16p13.3 microdeletions or mutation in gene for CREB
binding protein found in this area (19%)
- Also 22q13:
E1A
binding protein
Other Findings
- Postnatal growth retardation
- Males 153 cm average
- Females 147 cm average
- Microcephaly
- Agenesis of Corpus Callosum
- Seizures
- Hypoplastic maxilla, micrognathia
- Beaked nose, deviated septum
- PDA, ASD, VSD
- Capillary Hemangiomas
- Sternal anomalies
- Hypospadias, Cryptorchidism
- Hirsutism
- Spina Bifida
- Syndactyly, Polydactyly
- Keloid formation
References
- OMIM
#180849
- Wright, Spiegel eds. Pediatric Ophthalmology and
Strabismsus 2nd ed. p 1051
- Ocular features in Rubinstein-Taybi
syndrome: investigation of 24 patients and review of the literature. van
Genderen MM et al. BJO 2000 Oct;84(10):1177-84 (photo)
Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome (Acrocephaloysyndactyly type 3)
Smith-Magenis
Syndrome
Main Features
- Self Destructive Behavior (onychotillomania,
wrist-biting, head-banding, foreign bodies in ears)
- Mental Retardation
- Sleep Distrubance
- Brachycephaly, midface hypoplasia, prognathism
Eye Findings (abnormalities in 85%)
- Strabismus
- Myopia (-1.75 to -22.0)
- Anterior Segment
- microcornea
- Iris Abnormalities
- Spots (Brushfield Spots, Wölfflin-Krückmann spots)
- Hypoplasia
- Correctopia
- Posterior Segment: Retinal Detachment (probably related to high myopia and
head-banging)
Etiology
- Chromosome Deletion: 17p11.2
- Deletion found in perepherial blood with
cytogenic analysis/ flourescence in situ hybridization
Other Findings
-
Hoarse,deep voice
- Speech Delay
- Hearing loss
- Hyperactivity
-
Brachydactly
- Signs of peripherial neuropathy:
- Decreased or absent deep tendon reflexes
- Pes planus or pes cavus
-
Decreased pain sensitivity
- Decreased leg muscle mass
- Brain Ventriculmegaly
- Duplication of renal collecting system
- Low immunoglobulin levels
References
- Finucane BM, Jaeger ER, et al. Eye Abnormalities
in the Smith-Magenis Contiguous Gene Deletion Syndrome. Am J Med Genet.
45:443-446. 1993.
Thalassemia
Main Features
- Hypochromic and microcytic anemia, skin pallor and hepaosplenomegaly
Eye Findings
- Angioid Streaks (1.2%)
- Decreased Vision (15%)
- Degeneration of retinal pigment epithelium ("Salt and Pepper" macula)
(25%)
- May be associated with iron chelation therapy
- Deferiprone and desferrioxamine used for chelation
- More likely if patient had splenectomy
- Lens opacities (6%)
- Retinal venous tortuosity (78%)
Etiology
- Inherited disorder of hemoglobin synthesis
- Uncommon in US, more common in Middle East and Asia
References
- Taher A, et. al. Ocular Findings Among Thalassemia Patients. Am J
Ophthal. 142(4): 704-5. 2006.
- Gartaganis S. et al. Ocular abnormalities in patients with beta
thalassemia. Am J Ophthalmol. 108(6): 699-703. 1989.
-
http://www.emedicine.com/PED/topic2229.htm
Treacher-Collins-Franceschetti Syndrome (Mandibulofacial
dystosis)

Main
Features
- Bilateral characteristic facial features: malar
and mandibular hypoplasia, microstomia, coloboma of outer third of lower lid,
external and middle ear anomalies
Eye Findings
- External: lateral canthus
displaced downward (antimongolid slant)
- Lids: Coloboma of outer 1/3 of
lower lid, lack of cilia of medial lower lid, absence of lower puncta, absence
of meibomian glands
-
Iris: coloboma
- Motility: Esotropia
Etiology
- Autosomal Dominant
- Mutation in the 'treacle' gene (TCOF1; 606847)
- Gene map locus 5q32-q33.1
- 35 total reported mutations which represented a
detection rate of 60%
- Incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity
Other Findings
- Zygomatic bone may be absent
- Conductive hearing loss
- Cleft palate
- Normal intelligence
References
-
Dixon,
M. J. : Treacher Collins syndrome. Hum. Molec. Genet. 1996:
1391-1396, 1996
- OMIM: #154500
- Photo: American Academy of Ophthalmology
Wilson Disease (Hepatolenticular
degeneration)
Main Features
- Excess copper build-up tissues due to decreased
liver production of ceruloplasmin
Eye Findings
- Copper build up in Decemet's membrane of cornea:
Kayser-Kleischer ring
- Begins in superior and inferior limbus and works
it's way down to interpalpebral fissure
- Lens copper deposition possible
Etiology
-
Autosomal recessive
-
mutations in ATP7B gene (13q14.3-q21.1)
Other Findings
- chorea, dementia
- Parkinsonism
- speech deficits
-
renal failure
- liver failure,cirrhosis
-
Treatment: systemic D-penicillamine,
trientine, or zinc acetate for both ocular and systemic deposition
References
- Wright, Spiegel eds. Pediatric Ophthalmology and
Strabismsus 2nd ed. pp 406-7
- OMIM: #277900
Syndromes:
Index of Eye findings
Astigmatism
Cataract
Cherry-Red Spot
Choroiretinal coloboma
Esotropia
Exotropia
Foveal Hypoplasia
Hyperopia
Hypertelorism
Iris abnormalities (see iris coloboma)
Iris Coloboma
Lid Coloboma
Lid Abnormalities
Microcornea
Megalocornea
Microphthalmos
Myopia
- Aberfield syndrome
- Achard syndrome
- Achromatopsia
- Albinism
- Alport syndrome
- Anterior lenticonus
- Autosomal dominant cataract and microcornea
-
Bilateral blepharoptosis, ectopia lentis and
high myopia syndrome
- Choroideremia
- Chromosome 18 partial deletion (long-arm)
syndrome
- Clefting syndromes
- Coloboma
- Congenital external ophthalmoplegia
- Congenital scleral ectasia
- Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- Ectopia lentis
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Fabry's disease
-
Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy
-
Forsius-Eriksson syndrome
- Fundus flavimaculatus
- Gansslen Gänsslen syndrome
- Gillum-Anderson syndrome
- Gyrate atrophy
- Haney-Falls syndrome
- Hereditary ectodermal dysplasia syndrome
- Hereditary retinal detachment
- Homocystinuria syndrome
- Hypomelanosis of Ito syndrome
- Hypoparathyroidism
-
Kartagener syndrome
- Kenny syndrome
- Keratoconus
- Kniest's disease
- Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl syndrome
-
Marchesani syndrome
- Marfan syndrome
- Marshall
syndrome
- Matsoukas syndrome
- Meyer-Schwickerath and Weyers
(oculodentodigital) syndrome
- Microcornea
- Microphakia
- Microphthalmia
- Myasthenia gravis
- Myelinated nerve fibers
- Noonan syndrome
- Nystagmus with or without amblyopia
- Obesity-cerebral-ocular-skeletal anomalies
syndrome
- Oculodental syndrome
- Pierre Robin syndrome
- Pigmentary ocular dispersion syndrome
- Progressive bifocal chorioretinal atrophy
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Retinopathy of prematurity
- Riley-Day syndrome
- Schwartz syndrome
-
Smith-Magenis
Syndrome
- Vitreoretinal dystrophy
- Wagner's disease
Nystagmus
Optic nerve coloboma
Posterior Embryotoxin
Ptosis
Scleral Abnormalities
Retinal detachment
Retinal Lacunae
Retinal Pigmetary Degeneration
Strabismus
Supranuclear oculomotor palsy
![]()

